Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers organizations unparalleled scalability and flexibility to meet modern business demands. While AWS ensures the security of its underlying technology and services, customers are responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud. Proper configuration is essential to making an AWS environment resilient against cyber threats, and it’s more important than ever.
One of the simplest ways for organizations to assess their AWS security posture is the Center for Internet Security’s (CIS) benchmarks. AWS CIS benchmarks are documented best practices that provide straightforward checks to identify gaps in the security configuration of your AWS services.
Ready to learn more about all aspects of the AWS CIS benchmark?
What are the AWS CIS Benchmarks?
The AWS CIS Foundations Benchmark is a compliance standard that provides guidelines specifically for hardening and monitoring AWS accounts. Developed by the Center for Internet Security (CIS) who has a mission to make cyberspace safer by “developing, validating, and promoting timely best practice solutions.” Developed by a global community of security experts for securely configuring IT systems, software, and networks, the benchmarks are the global standard for improving organizations’ security and compliance posture.
AWS CIS compliance is important because cloud misconfigurations are a leading factor in data breaches and other cybercrimes. In fact, the benchmark enables cloud-based organizations to ensure their IT infrastructure is safeguarded against threats and attacks.
The AWS CIS benchmark provides guidelines for configuring the security options of foundational AWS services. These include:
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- AWS Config, AWS CloudTrail
- AWS CloudWatch
- AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS)
- AWS Simple Storage Service (S3)
- AWS VPC
The benchmark organizes the services into four sections: AWS CIS IAM Benchmark, AWS CIS Logging Benchmark, AWS CIS Monitoring Benchmark, and AWS CIS Networking Benchmark.
What Security Does AWS Provide?
AWS provides a range of security tools and features similar to the controls organizations deploy in their on-premises infrastructure. The company groups these into five categories:
Infrastructure security
Infrastructure security includes network firewalls built into Amazon VPC, private or dedicated connectivity options, DDoS mitigation technologies, automatic encryption of all traffic on the AWS global and regional networks between AWS secured facilities, and other tools to increase privacy and control network access.
Inventory & configuration management
This includes deployment tools for managing the creation and decommissioning of AWS resources; tools to identify AWS resources and track and manage changes to those resources over time; and tools to create standard, preconfigured, hardened virtual machines for EC2 instances.
Data encryption
Includes tools to encrypt data at rest; flexible key management options; dedicated, hardware-based cryptographic key storage; and encrypted message queues for the transmission of sensitive data.
Identity and access control
AWS provides the tools to define and enforce user access policies across AWS services through AWS Identity and Access Management, AWS Directory Service, and AWS IAM Identity Center.
Monitoring and logging
Monitoring and logging includes AWS CloudTrail, Amazon CloudWatch, and Amazon GuardDuty to give organizations visibility into their AWS environments. This helps identify issues before they impact the business and reduce their security risk.
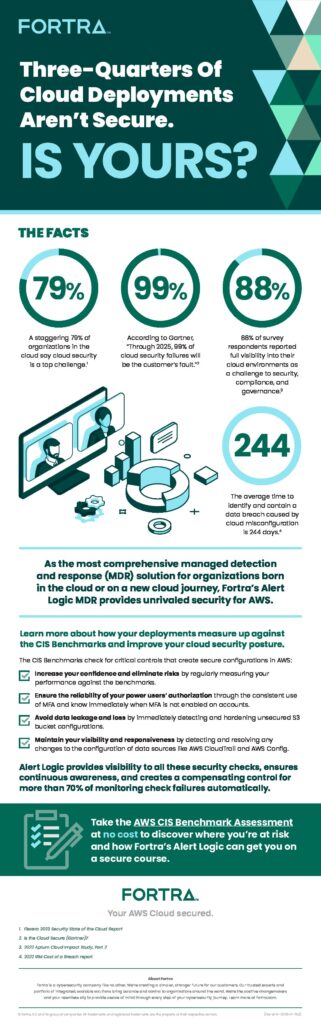
In response to the ever-increasing adoption of AWS, CIS developed several benchmarks to help configure many of these AWS services more securely. Before we jump into the details, take a look at the infographic below for an overview of the importance of securing AWS.
What is the AWS CIS Benchmark?
In general, new software installations come with default settings. All the services apps may be turned on, for example, or all its ports open. These out-of-the-box installations are extremely insecure. CIS benchmarks define best practices for configuring IT systems to meet industry cybersecurity standards. Currently, there are over 100 benchmarks across more than 25 products from AWS, Microsoft, Cisco, IBM, and other vendors.
Organized into two profile levels, the benchmarks help meet organizations’ immediate and long-term needs:
- Level 1: Designed to be implemented easily so organizations can quickly reduce their attack surface while maintaining normal operations. Guidelines with a Level 1 profile represent the minimum level of security and compliance all organizations should meet.
- Level 2: These recommendations address deeper defense. Level 2 is more costly and laborious to implement and can adversely impact the organization if not done correctly. Level 2 is for environments where security is of paramount importance.
Every benchmark is the product of input from a global community of security and IT professionals and goes through a two-step consensus review. First, a panel of the community members creates and tests the recommendations. Then the larger community reviews the recommendations and provides feedback, which is incorporated into the final standards.
All CIS benchmarks are available as PDF documents on the CIS website. Some benchmarks run over 800 pages, but they all follow the same basic structure.
Each benchmark starts with an overview addressing definitions and the benchmark’s intended audience. Recommendations for ensuring the correct configuration of an IT system make up the bulk of the document. Finally, the benchmark ends with a checklist appendix to help monitor compliance for each recommendation.
There may be hundreds of recommendations in a single benchmark. Each recommendation includes a description, the reason for the guideline, its potential security impact, and instructions on how to implement it. Recommendation classifications are “scored” or “not scored.” The scored recommendation contributes to an overall benchmark score and is required to achieve CIS compliance. However, recommendations without scores do not impact the overall benchmark score.
What are CIS Controls?
CIS controls are sets of broader security guidelines beyond asset configuration. Offered separately from CIS benchmarks, every benchmark recommendation maps to at least one CIS control.
The controls provide actions organizations can take to mitigate the damage from cyberattacks. There are 20 controls in all, organized into three categories to guide implementation. Basic CIS controls provide guidelines for preventing unauthorized hardware and software from accessing the network, controlling administrative privileges, and identifying and fixing system vulnerabilities. Foundational CIS controls deal with email and web browser protections, malware defenses, boundary defense, and data recovery. Organizational CIS controls cover security awareness and training programs, application software security, incident response and management, and penetration tests and red team exercises.
Further prioritization of the controls allows organizations to determine which actions to take based on risks and resources. First, Group 1 includes small organizations with low data sensitivity and/or limited resources. Group 2 is for larger organizations with multiple more complex IT systems and compliance requirements. Finally, Group 3 represents complex organizations with high-data sensitivity and strict compliance requirements.
The main difference between CIS benchmarks and CIS controls is benchmarks provide guidance for specific products and systems and the controls address the whole IT infrastructure. With the fact that every benchmark recommendation is mapped to at least one CIS control, organizations gain an understanding of how each one affects the larger security effort.
What is CIS Compliance?
CIS compliance is achieved by correctly implementing the best practice recommendations in a particular CIS benchmark. While it’s possible to implement benchmark recommendations manually, it’s time-consuming and error prone. For that reason, most organizations opt to use an automated solution. These third-party tools can scan a system or product to identify and alert the organization to areas of non-compliance and provide clear guidance on how to configure them to meet benchmark recommendations. Regular or continuous scans alert the organization to misconfigurations that get introduced over time so corrective action can be taken quickly and compliance maintained.
Who Should Use the AWS CIS Benchmarks?
As a leader in AWS security services, Fortra’s Alert Logic offers a free assessment of 49 best practice controls based on the industry-standard AWS CIS Benchmark. It includes a summary report of your AWS posture and how your AWS security measures compare to the CIS benchmarks. Alert Logic provides a list of remediating actions you can take and suggestions to ensure ongoing visibility. Best of all, Alert Logic does all the work so you can focus on your company’s daily business.
Additional Resources:
AWS Security Simplified: Support for the Shared Responsibility Model
Schedule an Alert Logic demo to see for yourself how we protect AWS workloads