During April 2019, Fortra’s Alert Logic research teams began tracking exploit attempts affecting users of Oracle WebLogic which could allow an attacker to run malicious software remotely.
An unauthenticated remote code execution in Oracle WebLogic allows attackers to remotely control victim hosts and execute code, install persistence and laterally move throughout the network. Exploit code has been released into the public domain and we have observed active attacks against our customer base using this vulnerability. This vulnerability can also be referred to as CNVD-C-2019-48814.
You may be affected if you run version 10.3.6.0.0 or 12.1.3.0.0 of Oracle WebLogic Server. Oracle has released a patch to mitigate this threat.
Alert Logic customers using our managed Web Application Firewall are protected from this threat.
Basically, a package that is included by default in some versions of WebLogic and provides communication services has a flaw when deserializing input information, an attacker can send a malicious HTTP request to gain the permissions of the target server and execute the command remotely without authorization.
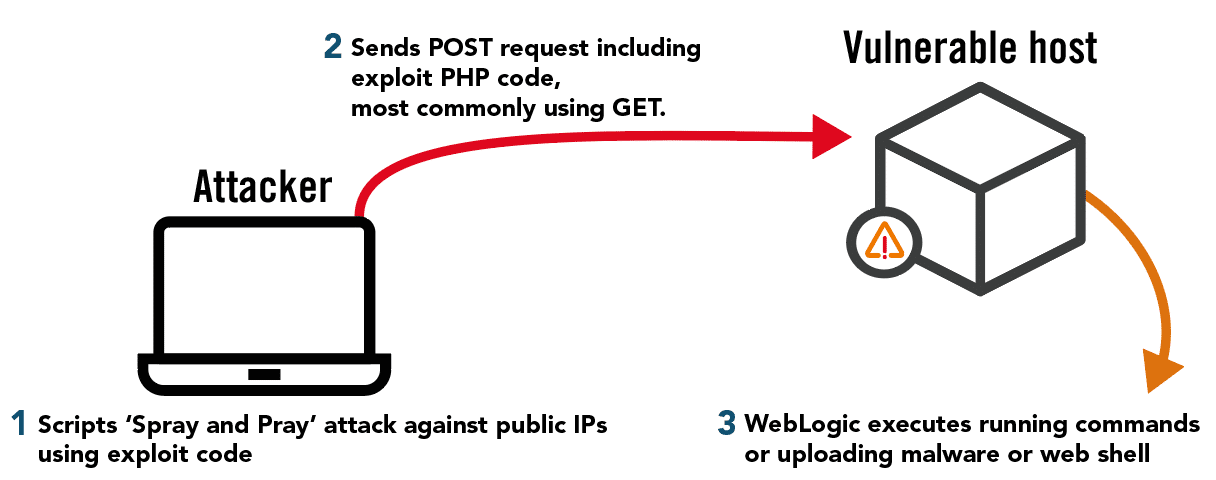
Attack Steps
1. Attacker incorporates exploit code into existing scripts to “fire and forget” exploit at public IP ranges
2. Sends request with exploit code, usually uploading persistent access mechanism, e.g. a webshell, working through success indicators from script output.
3. Oracle WebLogic will run the code and perform whatever action the attacker wants
What is a Webshell?
A webshell is a script or web page that enables remote administration of the underlying machine by a remote user. Most webshells are written in languages known to be supported by most web servers, e.g. PHP, Python, Ruby, Perl and ASP.
The shell gives the user the ability to create, edit, delete or download files, meaning that data on the system is at high risk of exfiltration and it is possible to upload and execute more specific or targeted code for disruption.
Timeline
| April 17, 2019 | Vulnerability initially disclosed on the CNVD but no exploit code was available making it uncertain if the vulnerability could actually be exploited. The vulnerability affects all versions of WebLogic.
http://www.cnvd.org.cn/webinfo/show/4989 In lieu of a patch the announcement identified mitigating steps as Delete the war package and restart WebLogic; Control access to the URL of the /_async/* path through the access policy. |
| April 21, 2019 | The KnownSec 404 Team publish a blog about exploiting the vulnerability |
| April 24, 2019 | Telemetry signature data shows attempts to exploit the vulnerability |
| April 26, 2019 | Oracle release a patch for the vulnerability (outside of their usual patch schedule, indicating the severity of the vulnerability)
https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/security-advisory/alert-cve-2019-2725-5466295.html |
| Alert Logic content teams released a signature to detect attack traffic specifically for this vulnerability. Analysis of this traffic using SOC tooling indicated that attackers are attempting to exploit the vulnerability. | |
Classified as Emerging Threat to formalize next steps
|
|
| Web Application Firewall blocking coverage confirmed for customers running in protect mode | |
| Scanning team and Major Incident Management identify list of customers running WebLogic, who are then contacted. | |
| Vulnerability Scanning coverage deployed, marked as a PCI Audit fail for reporting and auditing | |
| Knowledge Base Article published | |
| Broader customer communications sent | |
| May 1, 2019 | This blog published |
| Next Steps | SOC heightened awareness continues |
| Incident content released for automatic enriched incident generation. |
Exploit Details
A highly critical remote code execution vulnerability has been discovered in the wls9_async_response package, which is included by default in some versions of Oracle WebLogic and provides asynchronous communication services for WebLogic Server. This vulnerability allows for remote attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable servers.
Using this behavior attackers can cause victim hosts to fetch remote payloads – A remote code execution vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the victim box. This is likely to consist of commands to download and install persistence, such as malware or web shells. These malicious payloads could then be used to provide remote control over the victim host and allow further attacks (such as data exfiltration) or lateral movement on to other hosts in the network. This vulnerability allows attackers to eventually take over complete control of a vulnerable host once exploited.
When Was this Discovered/Published and Who Published it?
The vulnerability was initially disclosed on the CNVD but no exploit code was available making it uncertain if the vulnerability could actually be exploited. The vulnerability affects all versions of WebLogic.
http://www.cnvd.org.cn/webinfo/show/4989
The vulnerability was confirmed officially by Oracle on April 26, 2019, as CVE-2019-6340 / SA-CORE-2019-003, https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/security-advisory/alert-cve-2019-2725-5466295.html
Impact
There are no public reports, at the time of writing, of specific businesses that have been affected by the threat, however hundreds of attack attempts for this vulnerability against Alert Logic customers have been observed so assume attempts are being made across the public IP ranges.
Patches
Available via the Oracle Security Advisory linked above, due to the severity of this vulnerability, Oracle is strongly recommending that customers apply the updates provided by the Advisory as soon as possible.