Determining “Responsibility” for Cloud Security
Every day, more organizations are embracing cloud-first strategies, migrating key business operations to public cloud systems. What was once a hesitation — security concerns slowing down cloud adoption — is now a distant memory. Recent market forecasts predict global spending on public cloud services and infrastructure to soar to a staggering $809 billion by 2025, signaling that companies moving to the cloud are fully embracing the advantages of the public cloud. They’re managing potential security risks by mastering cloud security models and making smart, strategic shifts.
As businesses of all shapes and sizes flock to the cloud, they’re tapping into cutting-edge cloud security tools and services to enhance their existing defenses. But beware—these tools can create a false sense of security if companies don’t rework their security strategies to fit the cloud landscape. It’s critical for organizations to understand the ever-expanding attack surface, strategically use cloud providers’ tools, and reinforce their security with third-party services, lightening the load on internal teams and keeping threats at bay.
When Cybercriminals Strike Customer Vulnerabilities.
Capital One banking firm experienced a massive breach that exposed the personal and financial data of 98 million of its users. A former employee was indicted in connection with the crime, as well as for breaching thirty other organizations.5 The hacker reportedly used a server-side request forgery (SSRF) attack to access the data through a customer-side misconfiguration of the customer’s open-source web application firewall (WAF).
Following the announcement, Amazon confirmed that “AWS was not compromised in any way and functioned as designed.”6
Meanwhile, Capital One’s shares fell 10%, while steps taken to notify victims and offer free credit monitoring and identity protection costs exceeded US$190 million. Capital One paid an additional US$80 million in penalties tied to regulations.7
Test Your Knowledge
Can you correctly identify who is responsible for security in these areas?
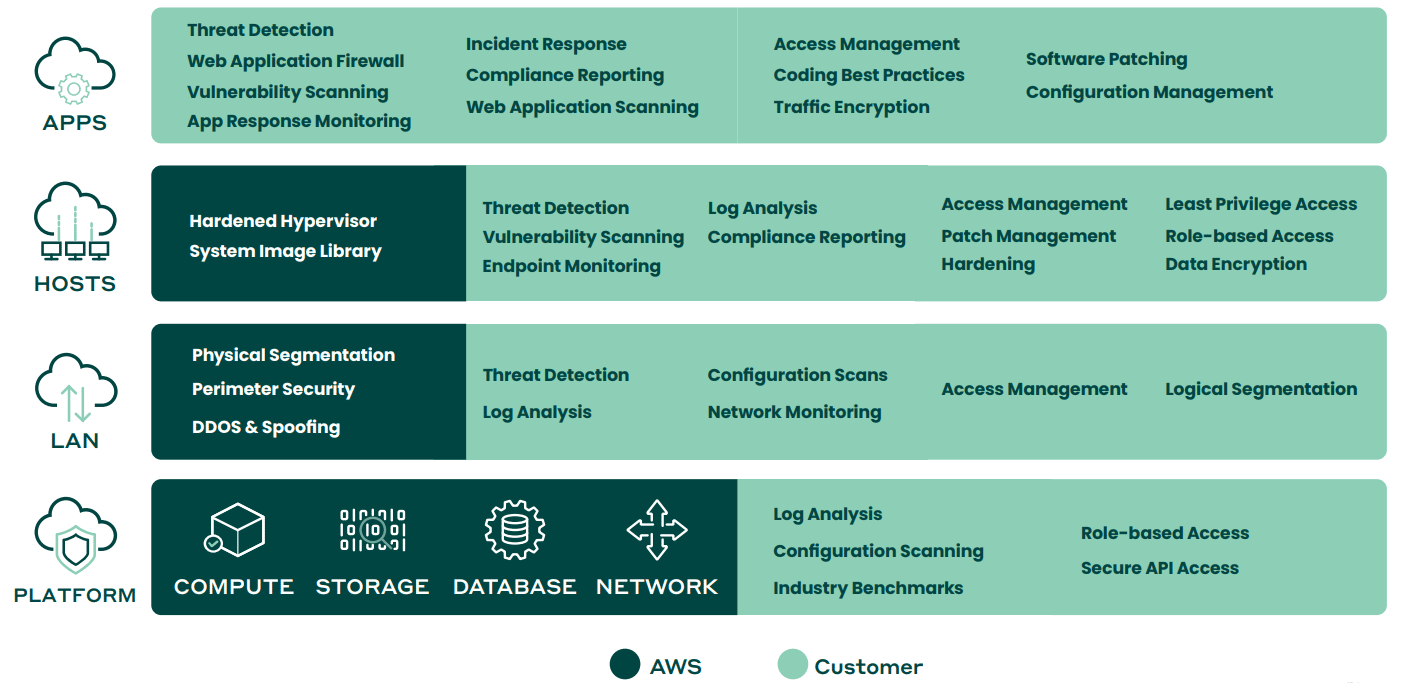
The Shared Security Responsibility Model (SSRM)
With AWS, security is a shared — but separate — responsibility. Based on the shared security responsibility model (diagram 1), AWS takes responsibility for the physical security of the infrastructure, networks, and foundational services. Meanwhile, the onus is on the customer to correctly deploy and maintain the security of everything within their AWS environment. This includes configurations, installations, administration, and ongoing upkeep, not to mention their own intra-organizational protection and privacy protocols.
Anything the customer loads or does via AWS is their responsibility. As such, it stands to reason that when customers use AWS for their data-driven business activities, their protection protocols shouldn’t look and feel too different from security processes used for securing data hosted on-premises or in secure data centers.
However, because the common, overarching assumption is that public cloud providers are protecting their platforms as well as all of the activities and customer data hosted there, it’s easy to lose sight of the fact that customers are equally, if not even more accountable, for protecting their cloud-based business. And when customers neglect to keep up their side of the SSRM, they’re putting their businesses at risk from potential vulnerabilities that come with the cloud’s larger attack surface.
What You Don’t Know About Your Cloud Security Can Definitely Hurt Your Business and Your Users
While the cloud itself is not inherently risky, it’s the areas that customers often overlook from a security perspective that open them up to potential exploitation from cybercriminals.
Just as Cloud Technology Continues To Evolve, So Too Do Cybercriminals’ Techniques. Today’s cybercriminals use increasingly sophisticated methods to find and infiltrate vulnerable systems. Customer SaaS applications are especially vulnerable to attacks. At the same time, the containers used to host cloud-based servers, databases, and the like also are highly susceptible to potential vector attacks8, including OS exploits, container breakouts, denial of service, embedded malware, and credential theft9 that occur when customer-side configurations, access management, and settings aren’t updated on a regular and frequent basis.
Cyberattacks Hit Organizations of all Sizes and Types. Nearly half of all cyberattacks are committed against small businesses, according to Verizon’s annual Data Breach Investigations Report.10 For SMBs, security remains the top cloud challenge closely followed by lack of resources and expertise.11 Misconfigurations are one of the leading attack vendors for organizations12 and can and can lead to costly security vulnerabilities. Lack of adequate controls and oversight as well as lack of awareness of security policies are the leading causes of misconfigurations in cloud environments.13 Most commonly experienced issues include encryption-related misconfigurations and misconfigured security groups and orphaned resources,13 contributing to a heightened state of vulnerability.
What’s at Stake For Organizations? Ultimately, cybercriminals don’t have to work very hard to infiltrate poorly secured systems, including those hosted in the cloud. The result: Business and user data, security credentials, and other sensitive information become easy pickings on GitHub and the dark web.
A 5 S T E P P L A N
Use the SSRM to Build a Cybersecurity Plan to Future-Proof Your Cloud-based Initiatives
Given the increasing frequency of cyberattacks on businesses in all industries, cloud-first businesses should follow these five steps to build their cybersecurity plans, in order to future-proof their current and future AWS-based initiatives:
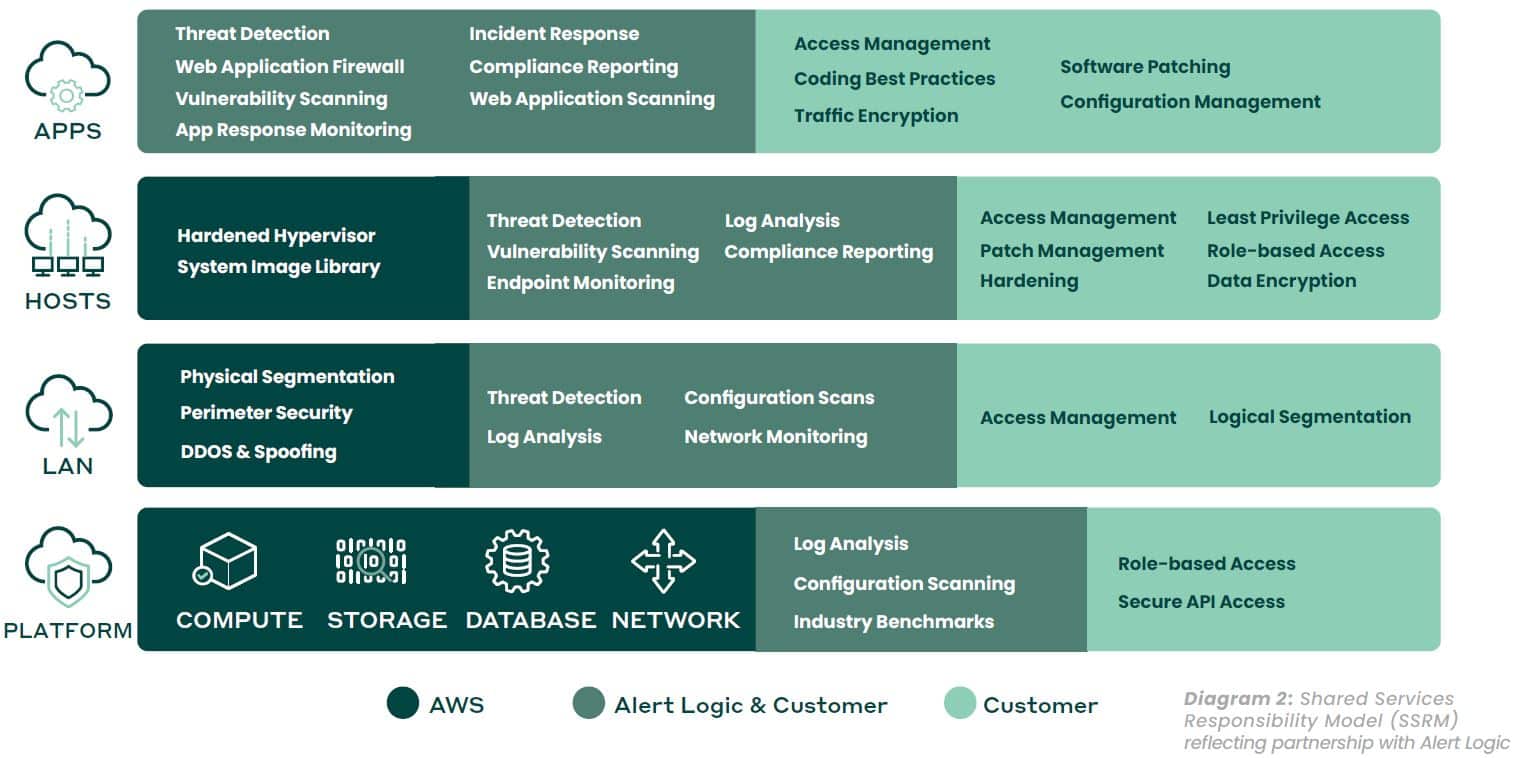
1. Assess your current security maturity level.
Using the SSRM as a foundation (diagram 2 reflecting partnering with Fortra’s Alert Logic), conduct an in-depth review of each layer of AWS cloud engagement, confirming the layers that you’re responsible for — especially focusing on the top three layers (e.g., apps, hosts, and networks) where customer involvement in security upkeep is most crucial.
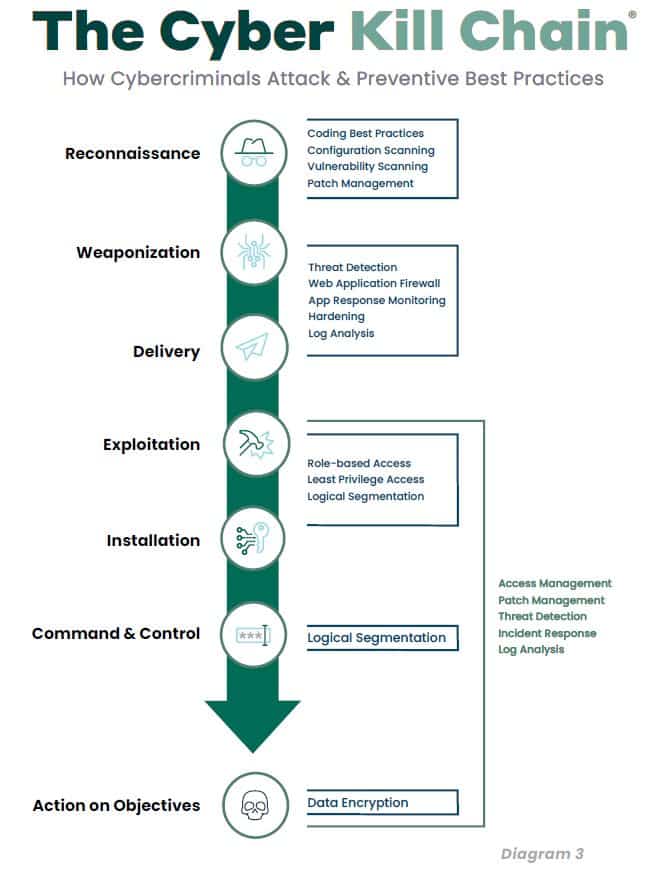
2. Determine action steps to fill in security gaps.
Based on your findings in Step 1, go through the four layers of the SSRM and identify the steps you’ll need to take to bolster your security protocols at each level, using the cyber kill chain (diagram 3) as a guide to prioritize increased protection measures where you need them most.
3. Prioritize security in all future development work.
Once you’ve established an action plan to mitigate vulnerabilities, we recommend that you take a page from the Privacy by Design playbook14 (the foundation upon which GDPR was developed15), and integrate security into the delivery pipeline at every stage of the development process, rather than it being left as an add-on module at the end.
4. Fortify your environments against future threats.
Consider integrating the following areas into your defense strategy for added protection of your cloud security attack surface:
Access Management:
- Maintain the principle of least privilege (POLP), limiting access rights for users to the minimum permissions they need to perform their work.
- Identify integrations, ensuring access is locked.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
A NOTE ABOUT FILLING GAPS IN YOUR SECURITY COVERAGE:
Depending on the extent of your in-house IT and operations capabilities, you may find it beneficial to work with a threat management provider, like Fortra’s Alert Logic, that combines industry-leading technology, cutting-edge intelligence, and expert people-power to future-proof every area of your evolving business, without having to take on the work and cost of building out your own security solutions.
Logical Segmentation:
- Segment cloud accounts according to data sensitivity, developing a variety of models, including multi-account, by app, and business units.
- Build logical network boundaries to boost performance and limit unauthorized traffic.
Monitoring:
- Early detection of exposures is key to mitigating risk from insecure configurations or new vulnerabilities that may crop up in the cloud.
- Continuous assessment of your environments is vital, as new vulnerabilities are uncovered every day, and not just after cloud provider-pushed system updates.
- Mitigate the impact of attacks with proactive monitoring of networks and applications for known and unknown threats (especially zero-day attacks) that can expose critical business data.
5. Socialize security across your organization.
Build a security-conscious culture, socializing the idea of “security in cloud-first” with all employees:
- Institute awareness training on an annual basis and after major incidents or business changes (e.g., system compromise, merger/acquisition, ERP implementation, new hires or fires).
- Train public-facing staff to recognize, handle, and report internal security infiltration attempts.
- Develop clear processes that employees can follow if they think they’ve detected security threats.
Expanding the Shared Security Responsibility Model
Expanding the Shared Security Responsibility Model
Organizations are moving to the cloud at an unprecedented rate. With the transition to the cloud comes additional responsibilities for these customers — to keep their configurations, installations, and intra-organizational protection and privacy protocols safe from crafty criminals who are waging more aggressive attempts to breach cloud-based infrastructure, systems, platforms, and applications.
Organizations of all sizes and types have the power to protect themselves and their users from cybersecurity threats by taking a proactive approach that keeps shared security responsibility of cloud platforms top of mind, now and in the future.
AWS provides the elasticity and agility businesses need to meet consumers demand at scale. Yet, shared cloud tenancy comes with certain responsibilities — including staying up to date on the latest privacy and protection protocols that can keep your business-critical applications safe from cyberattacks.
If you’re struggling to keep up, we can help! Learn more about Fortra’s Alert Logic’s integrated security approach for AWS and other cloud workloads here.
C O N T I N U E D L E A R N I N G
AWS Security Resources
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model Explained
A comprehensive breakdown of the AWS Shared Responsibility Model, including which security controls are AWS’s responsibility and which are the customer’s.
Alert Logic AWS Security Services
See how our award-winning, fully managed AWS Security solutions are designed to keep your Amazon Web Services environments safe and compliant.
AWS Cloud Migration Best Practices
Migrating to AWS? We’ve outlined several best practices and strategies to follow as you embark on your cloud migration journey.
9 AWS Security Best Practices
These 9 AWS security best practices will help you keep up with the fast-paced nature of building on the cloud.
SOURCES:
1. As suggested by studies cited in https://www.techrepublic.com/article/security-is-the-no-1-it-barrier-to-cloud-and-saas-adoption/, https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/ca/pdf/2018/03/cloud-computing-risks-canada.pdf, https://www.isc2.org/-/media/ISC2/Landing-Pages/2019-Cloud-Security-Report-ISC2.ashx?
2. https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS48208321
3. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/digital-mckinsey/our-insights/cloud-adoption-to-accelerate-it-modernization
4. https://www.computerweekly.com/news/252470022/CISOs-think-cloud-safer-but-security-fears-remain
5. https://www.wired.com/story/capital-one-paige-thompson-case-hacking-spree/
6. https://www.newsweek.com/amazon-capital-one-hack-data-leak-breach-paige-thompson-cybercrime-1451665
7. https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/capital-one-reaches-190-million-5708035/
8. https://containerjournal.com/topics/container-security/the-4-most-vulnerable-areas-of-container-security-in-2019/
9. https://info.flexera.com/CM-REPORT-State-of-the-Cloud
10. https://www.ibm.com/security/data-breach
11. https://resources.fugue.co/state-of-cloud-security-2021-report
12. https://www.oreilly.com/content/five-security-concerns-when-using-docker/
13. https://www.verizon.com/business/resources/reports/dbir/
14. https://www.ipc.on.ca/wp-content/uploads/resources/7foundationalprinciples.pdf
15. https://martech.org/privacy-design-deeper-dive-gdpr-requirement/